ShuffleNet
[reference]
논문 링크: ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices
- 2017년 7월
- Xiangyu Zhang, Xinyu Zhou, Mengxiao Lin, Jian Sun
Blog: https://hongl.tistory.com/38
목차
용어
- Depthwise Convolution: 기존 Standard Convolution과 달리 각 채널별로 Convolution 연산 진행 / 링크의 1-1, 1-2 참고
- Pointwise Convolution: 1x1 Convolution 연산. 연산방식이 Fully Connected Layer와 유사하여, Computational Cost 높음 / 링크의 1-3 참고
- Skip Connection: 일반적으로 Residual Network처럼 원본을 다시 더할 때 사용하는 Connection / 링크의 3 참고
요약
- MobileNetV2에서 사용했던 Depthwise Convolution과
- ResNeXt에서 사용하였던 Group Convolution을 이용하고
- 추가적으로 Pointwise Group Convolution을 이용하여, 연산량이 많은 Pointwise Convolution 대체
설명
1. Pointwise Group Convolution
- 기존의 Pointwise Covolution과 다르게 Group을 지어서 Pointwise Convolution 진행
- 다만 이렇게 진행할 경우 모든(Global) Channel이 아닌 지역적인(Local) Channel 묶음만 고려하게 되므로,
- 이를 해결하기 위해 이후에 설명할 Channel Shuffle 사용
1-1. 기존 Pointwise Convolution
채널의 수를 마음대로 조정할 수 있음
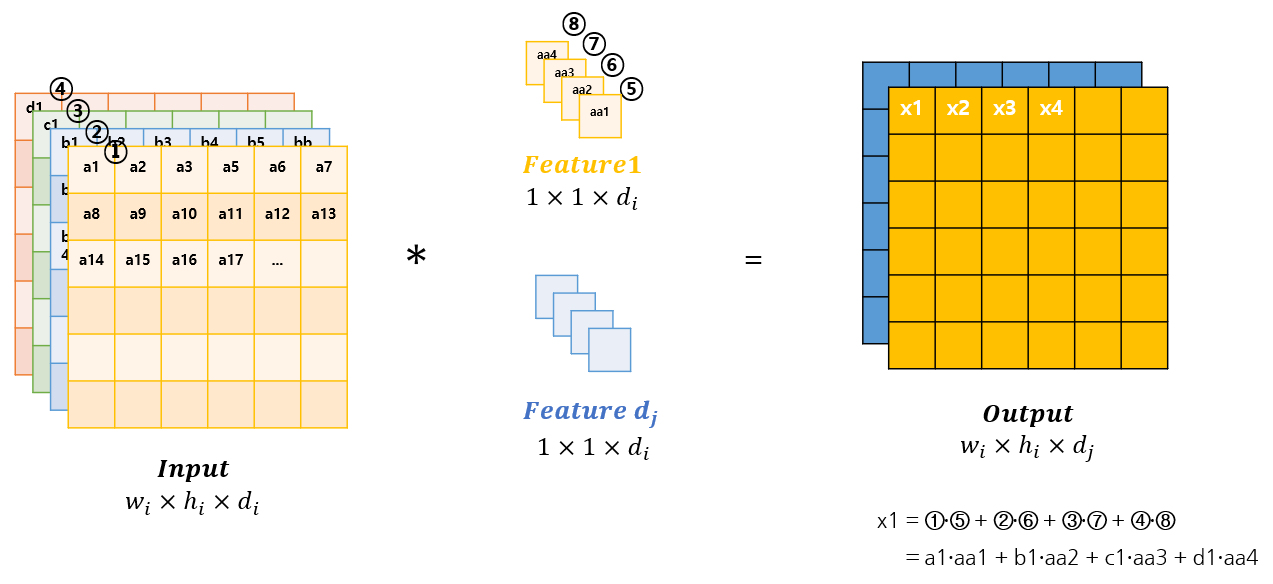
연산량은 다음과 같음
연산 발생
1-2. Group Pointwise Convolution
- 다음과 같이 Group을 지어서 Group 별로 각각 Pointwise Convolution 진행
- 연산방식은 1-1. 기존 Convolution 연산과 동일하나 Group을 나눠서 Group별로 Pointwise Convolution 연산을 진행함
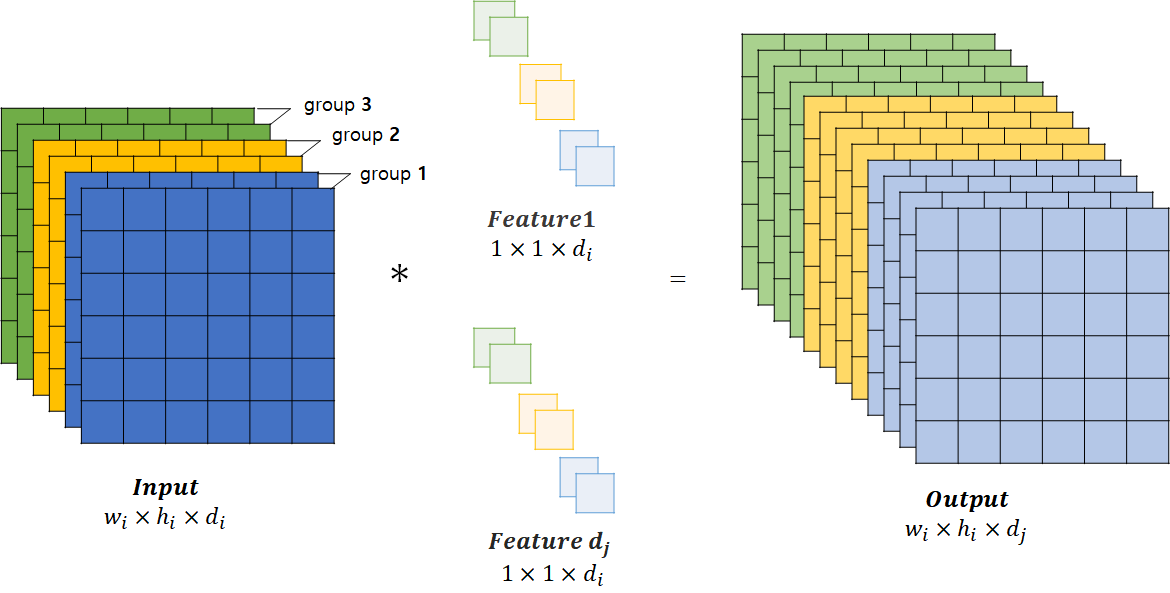
Group을 지어서 계산하므로, 계산량은 다음과 같음
개의 Group이 있다고 할 때, 한 Group당 연산 수 : Input Channel의 수 : Output Channel의 수
Group Poinwise Convolution의 총 연산 수는 Group의 수
만큼 곱해주면 되기 때문에 다음과 같음 Standard Pointwise Convolution의 경우에 비해
의 연산량 감소 하지만 전체적인 Channel을 고려하지 않고, 같은 Group 내에 있는 Channel들만 고려하기때문에, Representation power(표현력) 감소
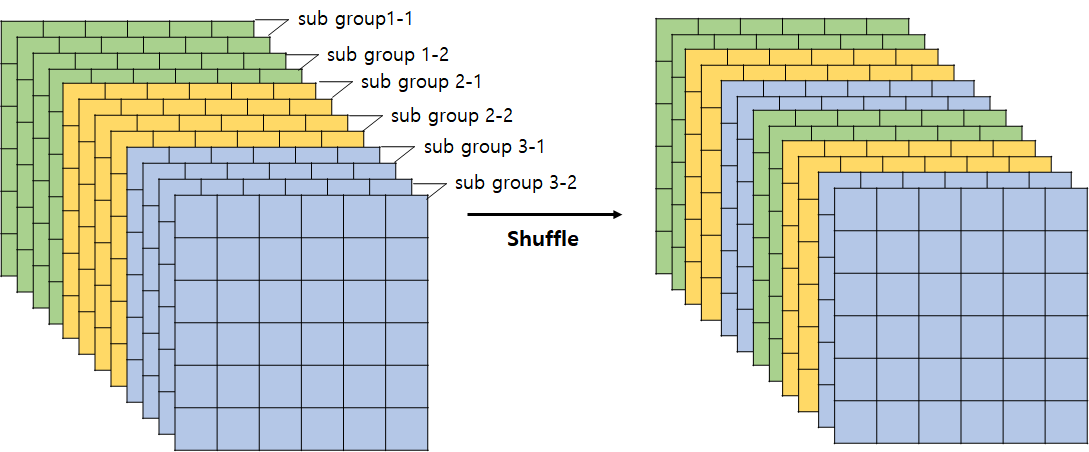
2. Channel Shuffle
Group Convolution 연산의 부작용(Group내에 있는 채널들끼리만 참고하다보니, 표현력이 약화되는 문제)를 해결하기 위해 고안된 방식
Group을 다시 Sub Group으로 나눠서 섞음(Shuffle)
이는 추후에 코드 구현을 진행하며 설명하겠지만,
개의 Group이 각각 개의 Channel을 가질때, 이를 차원의 Tensor로 만든 뒤, Transpose, flatten으로 쉽게 구현가능
3. ShuffleNet Unit
- 기본적으로 MobileNet에 Residual Connection을 추가한 형태로
- 세 가지 형태의 Unit을 만들어서 사용함
- (b), (c)의 처음 1x1 GConv에서 Bottleneck을 구현하는데, 이때 Bottleneck Channel의 수는 Output Channel의 1/4로 고정
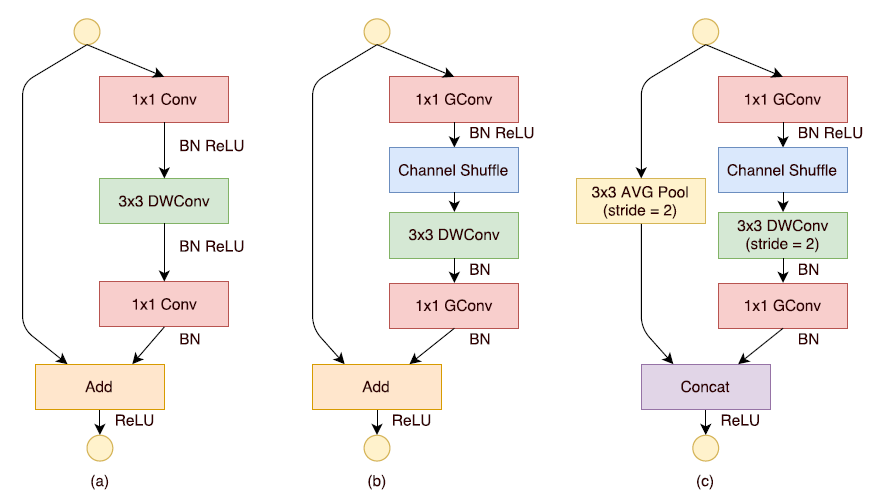
(a): MobileNet에 Residual Connection을 추가한 형태
(b): Pointwise Convolution을 Group Pointwise Convolution으로 대체 및 Channel Shuffle / 이때 Depthwise Convolution 진행 후, ReLU를 사용하지 않음
(c): (b)의 형태에서, DWConv시에 Stride=2로 주어 Image의 가로, 세로 사이즈를 반으로 줄임
Skip Connection에도 똑같이 Image의 가로, 세로를 줄이기위해 Stride 2의 Average Pooling 추가
마지막 1x1 GConv를 진행할 때 Channel의 수 목표하는 Output Channel의 수까지 Expand함 ((b)에서도 동일)
이후 목표하는 Output Channel의 수에서 입력했던 Input Channnel의 수를 빼줘서
이후 3x3 AVG Pooling 층을 Concatenate했을때의 Channel 수 보존
- 이렇게 진행하게 될 때, AVG Pooling 층의 Channel을 늘려서 더해주는 것보다 적은 연산량으로 처리 가능
4. Network Architecture
- ShuffleNet은 적은 연산량을 이용해 더 많은 Output Channel, 즉 적은 연산으로 더 많은 Feature를 얻을 수 있음
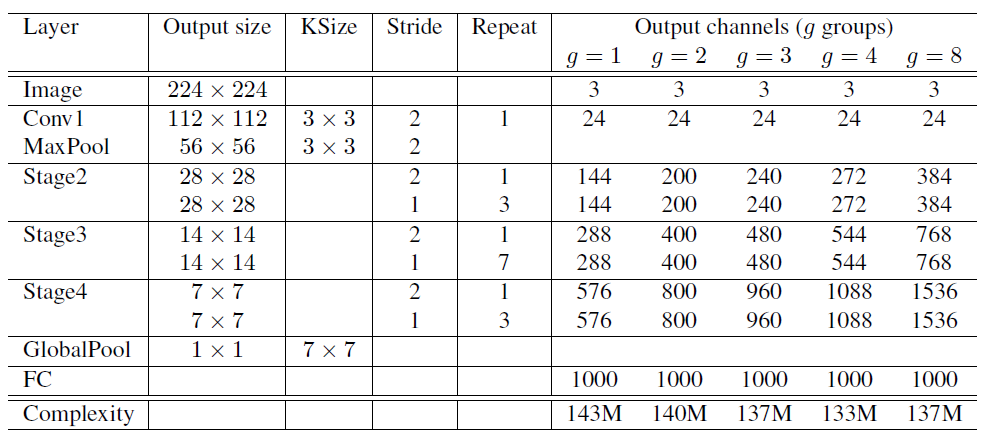
- Stride=2: 3. ShuffleNet Unit에서의 (c) Unit
- Output Channels: MAdds(연산량)을 고정시켰을 때, Group 값에 따라 Channel의 수를 얼마나 늘릴 수 있는지 표현 (더 많은 Feature 표현 가능)
5. Experiment
5-1. Group Pointwise Convolution의 효과
.png)
1x, 0.5x, 0.25x는 Filter(Channel)의 수를 Scalling한 것
Group의 수가 많을 수록 정확도 상승의 효과도 있음
은 기존의 Pointwise Convolution 연산
5-2. Channel Shuffle의 효과
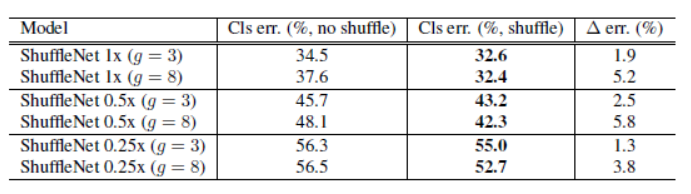
- Channel Shuffle을 진행하면, Group의 개수와 상관없이 Classification Error가 적어진 것을 확인할 수 있음
구현
Pytorch를 이용한 Code 구현시 필요한 기초개념은 다음의 링크를 참고
1. 코드
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from collections import OrderedDict # 딕셔너리에 넣는 순서를 보존
from torch.autograd import Variable
from collections import OrderedDict
from torch.nn import init
def channel_shuffle(x, groups):
batchsize, num_channels, height, width = x.data.size()
channels_per_group = num_channels // groups
# Tensor의 크기는 변하지 않는 상태에서 Reshape
# view()가 아닌 Reshape() 함수를 쓰게 되면, copy가 되거나 view가 되거나 둘중하나가 됨
# Channel를 Channel_per_group으로 축소시키고, Groups 차원을 추가ㅜ
x = x.view(batchsize, groups, channels_per_group, height, width)
# Transpose
# view쓰기전에 transpose()를 사용하는경우 contiguous 사용이 필요함
x = torch.transpose(x, 1, 2).contiguous()
# Tensor의 크기는 변하지 않는 상태에서 Reshape. 이때 -1은 값이 따로 정해지지 않았으니, 이쪽으로 남은 값들 배치됨
x = x.view(batchsize, -1, height, width)
return x
def conv1x1(in_channels, out_channels, groups=1):
# 1x1 Convolution with Padding
return nn.Conv2d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=1,
groups=groups,
stride=1
)
def conv3x3(in_channels, out_channels, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True, groups=1):
# 3x3 Convolution with Padding
return nn.Conv2d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=3,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
bias=bias,
groups=groups
)
class ShuffleUnit(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, groups=3, grouped_conv=True, combine='add'):
super(ShuffleUnit, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.bottleneck_channels = self.out_channels // 4 # @@
self.groups = groups
self.grouped_conv = grouped_conv
self.combine = combine
# 본문의 (b)구조
if self.combine == 'add':
self.depthwise_stride = 1
self._combine_func = self._add
# 본문의 (c)구조
elif self.combine == 'concat':
self.depthwise_stride = 2
self._combine_func = self._concat
self.out_channels -= self.in_channels # 이후 3x3 pooling층과 concat할때 output channel을 유지하기 위해 빼줌
else:
raise ValueError("Cannot combine tensors with \"{}\"" \
"Only \"add\" and \"concat\" are" \
"supported".format(self.combine))
# grouped conv Flag가 꺼져있으면 (= 첫번째면) 1로 설정
# 처음에는 False로해서 해야해
self.first_1x1_groups = self.groups if grouped_conv else 1
# 1x1 G Conv
self.g_conv_1x1_compress = self._make_grouped_conv1x1(
self.in_channels,
self.bottleneck_channels, # 최종 output_channel의 1/4 입력
self.first_1x1_groups,
batch_norm=True,
relu=True
)
self.depthwise_conv3x3 = conv3x3(
self.bottleneck_channels,
self.bottleneck_channels, # output수는 생성하는 Feature의 수에 따라 달라짐
stride = self.depthwise_stride,
groups = self.bottleneck_channels, # Group 수를 input수와 동일하게 하여, 각 채널별로 연산할 수 있게 설정
)
self.bn_after_depthwise = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.bottleneck_channels)
# 마지막 1x1 G Conv
self.g_conv_1x1_expand = self._make_grouped_conv1x1(
self.bottleneck_channels,
self.out_channels,
self.groups,
batch_norm=True,
relu=False
)
@staticmethod
def _add(x, out):
# residual connection
return x + out
@staticmethod
def _concat(x, out):
# concatenate along channel axis
return torch.cat((x, out), 1)
def _make_grouped_conv1x1(self, in_channels, out_channels, groups, batch_norm=True, relu=False):
modules = OrderedDict()
conv = conv1x1(in_channels, out_channels, groups=groups)
modules['conv1x1'] = conv # 딕셔너리에 저장
if batch_norm:
modules['batch_norm'] = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
if relu:
modules['relu'] = nn.ReLU()
if len(modules) > 1:
return nn.Sequential(modules)
else:
return conv
def forward(self, x):
# Skip Connection을 위해 미리 저장
residual = x
# Unit (c)의 경우
if self.combine == 'concat':
residual = F.avg_pool2d(
residual,
kernel_size=3,
stride=2,
padding=1)
out = self.g_conv_1x1_compress(x)
out = channel_shuffle(out, self.groups)
out = self.depthwise_conv3x3(out)
out = self.bn_after_depthwise(out)
out = self.g_conv_1x1_expand(out)
out = self._combine_func(residual, out)
return F.relu(out)
class ShuffleNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, groups=3, in_channels=3, num_classes=1000):
super(ShuffleNet, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.groups = groups
self.stage_repeats = [3, 7, 3]
# index 0 is invalid and should never be called.
# 편의를 위해 index 1번부터 작동하게 설정
if groups == 1:
self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 144, 288, 567]
elif groups == 2:
self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 200, 400, 800]
elif groups == 3:
self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 240, 480, 960]
elif groups == 4:
self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 272, 544, 1088]
elif groups == 8:
self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 384, 768, 1536]
else:
raise ValueError(
"""{} groups is not supperted for 1x1 Grouped Convolutions""".format(groups)
)
# stage 1은 항상 24개의 output channel을 가짐
self.conv1 = conv3x3(
self.in_channels,
self.stage_out_channels[1], # out_channels
stride=2
)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
# stage 2 ~ 4
self.stage2 = self._make_stage(2)
self.stage3 = self._make_stage(3)
self.stage4 = self._make_stage(4)
# Global pooling:
# Undefined as PyTorch's functional API can be used for on-the-fly
# shape inference if input size is not ImageNet's 224x224
# Fully-Connected Classification layer
num_inputs = self.stage_out_channels[-1]
self.fc = nn.Linear(num_inputs, self.num_classes)
self.init_params()
def init_params(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
# Weight Initialization 방식 중 He Initialization 방식이용
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def _make_stage(self, stage):
modules = OrderedDict()
stage_name = "ShuffleUnit_Stage{}".format(stage)
# 1. Stage 2까지는 Standard Pointwise Convolution만을 사용
grouped_conv = stage > 2
# 2. Concatenation unit은 항상 사용됨 / 본문의 (c) 형태의 Unit을 항상 사용
first_module = ShuffleUnit(
self.stage_out_channels[stage-1],
self.stage_out_channels[stage],
groups=self.groups,
grouped_conv=grouped_conv,
combine='concat'
)
modules[stage_name+"_0"] = first_module # 딕셔너리에 저장
# (b)형태의 ShuffleUnit을 사전에 설정된 반복횟수만큼 추가
for i in range(self.stage_repeats[stage-2]):
name = stage_name + "_{}".format(i+1)
module = ShuffleUnit(
self.stage_out_channels[stage],
self.stage_out_channels[stage],
groups=self.groups,
grouped_conv=True,
combine='add'
)
modules[name] = module
return nn.Sequential(modules)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.stage2(x)
x = self.stage3(x)
x = self.stage4(x)
# global average pooling layer
x = F.avg_pool2d(x, x.data.size()[-2:])
# Flatten for input to fully-connected layer
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # -1이 있는 부분으로 값이 다 몰림
x = self.fc(x)
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
model = ShuffleNet()
2. 결과
summary(model, (3, 224, 224))
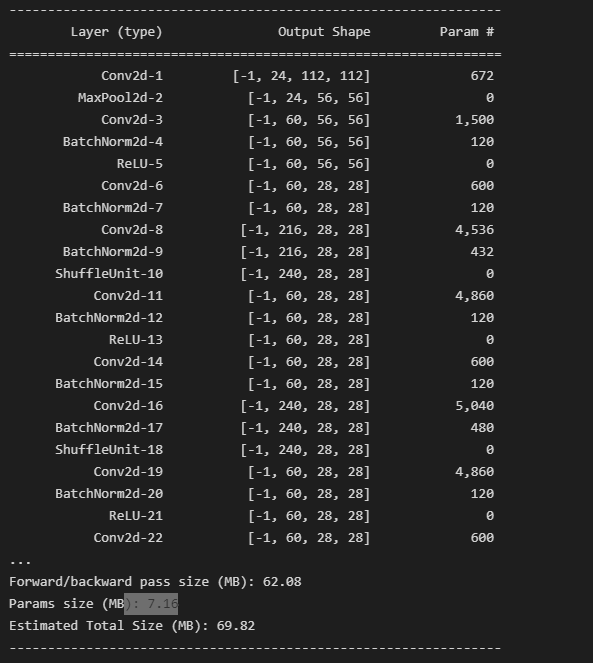
'Computer Vision' 카테고리의 다른 글
| NAFNet 쉬운 논문 리뷰 (0) | 2022.11.27 |
|---|---|
| MobileNetV3 쉬운 논문 리뷰 및 Pytorch 구현 (0) | 2022.08.02 |
| MnasNet 쉬운 논문 리뷰 (0) | 2022.08.01 |
| Squeeze-Excitation Network 쉬운 논문 리뷰/구현 (0) | 2022.07.19 |
| MobileNet V2 쉬운 논문 리뷰/구현 (1) | 2022.07.07 |




댓글